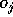 , known from the forward phase, and the expected nominal target value
, known from the forward phase, and the expected nominal target value 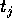 :
:
For the backward phase (figure 7) the neuron j in the output layer calculates the error between its
actual output value 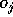 , known from the forward phase, and the expected nominal target value
, known from the forward phase, and the expected nominal target value 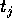 :
:
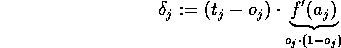
The error 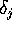 is propagated backwards to the previous hidden layer.
is propagated backwards to the previous hidden layer.
The neuron i in a hidden layer calculates an error  that is propagated
backwards again to its previous layer. Therefor a column of the weight matrix is used.
that is propagated
backwards again to its previous layer. Therefor a column of the weight matrix is used.
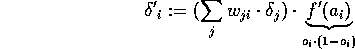
To minimize the error the weights of the projective edges of neuron i and the bias values in the receptive layer have to be changed. The old values have to be increased by:

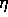 is the training rate and has an empirical value:
is the training rate and has an empirical value: 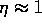 .
.
The back-propagation algorithm optimizes the error by the method of gradient descent,
where 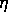 ist the length of each step.
ist the length of each step.